Siberian Cave Findings Shed Light on Extinct Human Species [View all]
January 30, 2019 8:14 PM
Reuters

WASHINGTON —
Scientists using sophisticated techniques to determine the age of bone fragments, teeth and artifacts unearthed in a Siberian cave have provided new insight into a mysterious extinct human species that may have been more advanced than previously known.
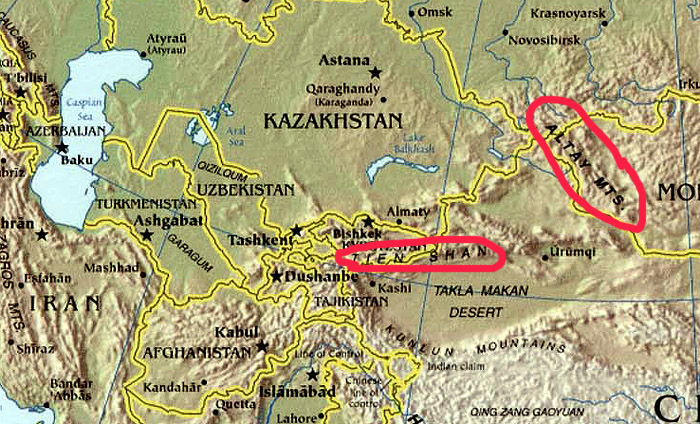
Research published Wednesday shed light on the species called Denisovans, known only from scrappy remains from Denisova Cave in the foothills of the Altai Mountains in Russia.
While still enigmatic, they left a genetic mark on our species, Homo sapiens, particularly among indigenous populations in Papua New Guinea and Australia that retain a small but significant percentage of Denisovan DNA, evidence of past interbreeding between the species.
Fossils and DNA traces demonstrated Denisovans were present in the cave from at least 200,000 to 50,000 years ago, and Neanderthals, a closely related extinct human species, were present there between 200,000 and 80,000 years ago, the new research found. Stone tools indicated one or both species may have occupied the cave starting 300,000 years ago.
More:
https://www.voanews.com/a/siberian-cave-findings-shed-light-on-extinct-human-species-/4766383.html
Amazing images of the Altai Mountains in Russia:
https://tinyurl.com/yc8akjws